The advanced, utilities workflow component, Database SQL update can be used in order to update or insert data in a table in a database.
Enabling custom SQL
Custom SQL needs to be enabled in the global System settings. It is divided into two sections:
Enable custom SQL selects.
Enable custom SQL updates.
Here you can enable/disable SQL selects and/or updates for all tenants. For this workflow element the update needs to be enabled.
Related components are: Enrich XML from database and Enrich spooled file from database. These functions will keep the original payload and add the retrieved data into the XML/spooled file in the payload.
Another related component is the Database SQL select.
A related workflow input is: From database with custom SQL, which starts a workflow with an SQL select.
A related function is the built-in function, ng:databaseLookup which can lookup in a database and return the found data.
Dangers of using custom SQL in InterFormNG2
SQL is a powerful tool, but it can cause severe performances issues in InterFormNG2.
The result XML node names are from the names of the columns in the result. If these nodes contains illegal XML node names, an error will happen. Use AS NAME (depending on SQL dialect) in the select to rename the columns. Example: select usern(a)me as username, cit(y) as city from customers - here (a) and (y) represents illegal xml characters.
SQL updates are committed automatically.
All values are treated as strings. This MIGHT be a problem with special columns such as blobs.
ALWAYS use the ? parameter replacement for dynamic data, since this is the safest option. This is especially true for data that are not machine generated. (E.g. a name entered on a website).
The parameters
The Database SQL update has these parameters:
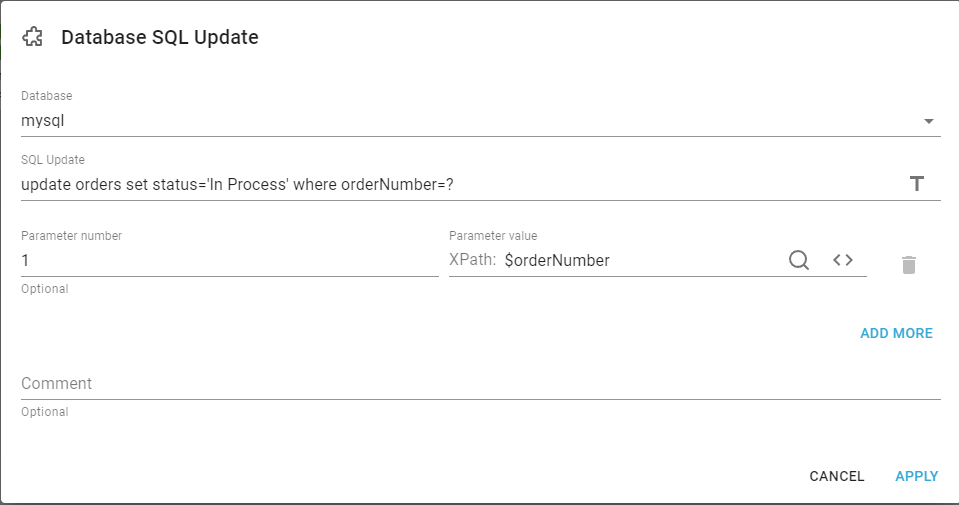
Database
This refers to an existing database connection, which has been setup for the tenant.
SQL Select
This selects the records from a table, that are to be extracted in this workflow. The workflow will convert the records into an XML file, which will be saved into the payload for further processing.
The same selection is executed again and again, so it is a good idea to consider to mark processed records with a specific status and exclude them in the selection.
The SQL is a standard SQL select statement, that is being executed as a prepared statement. This means that ? in the SQL will be updated safely with parameter number and parameter value.
The ? is in order in the SQL, where 1 is the first ? that is being replaced.
It is strongly recommended to use the ? parameter functionality to insert values that are dynamic, since this automatically prevents SQL injections and other nasty side effects of a raw SQL.
The job log will show how many rows that were updated.
Parameter number and Parameter value
This is the sequence number of the question mark (?), that is to be replaced in the SQL Select above. The number 1 means: Replace the first question mark with the parameter value stated on the same line. You can click the blue Add more link on the right to add additional parameters to match the number of question marks in the SQL statement above. You can delete a line with the trash can icon to the right of the line.
Here is another example:
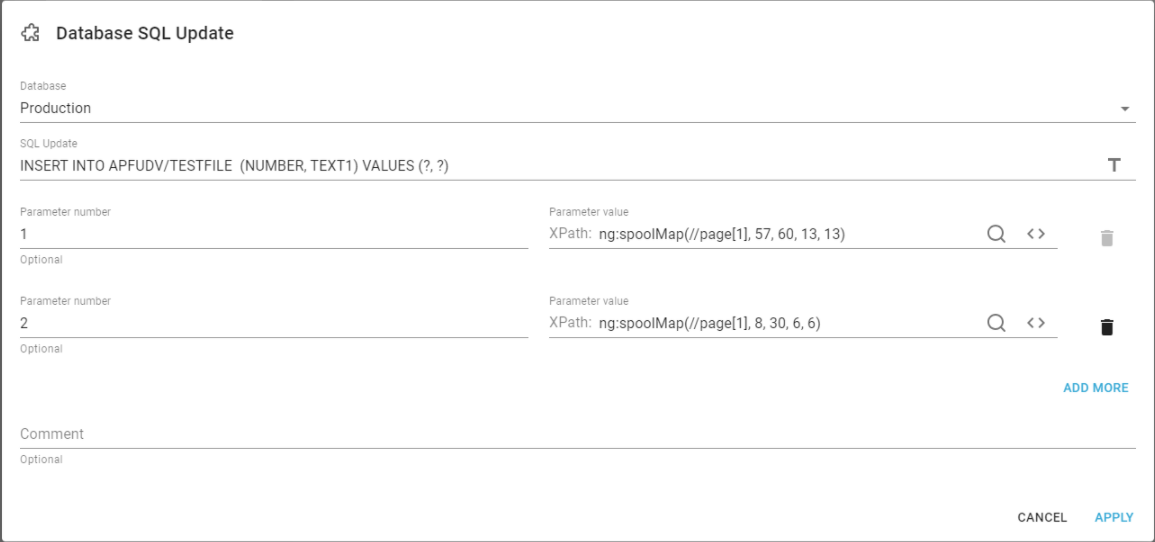
With the expression above the first question mark is replaced with the value found in page 1, position 57-60 in line 13 of the input spooled file. The second question mark is replaced with the value found in page 1, position 8 to 30 in line 6 of the input spooled file.
In this way we add a new record in the file, APFUDV/TESTFILE and the field, NUMBER gets the text found in page 1, position 57 to 60 in line 13 and the field, TEXT1 gets the other value.